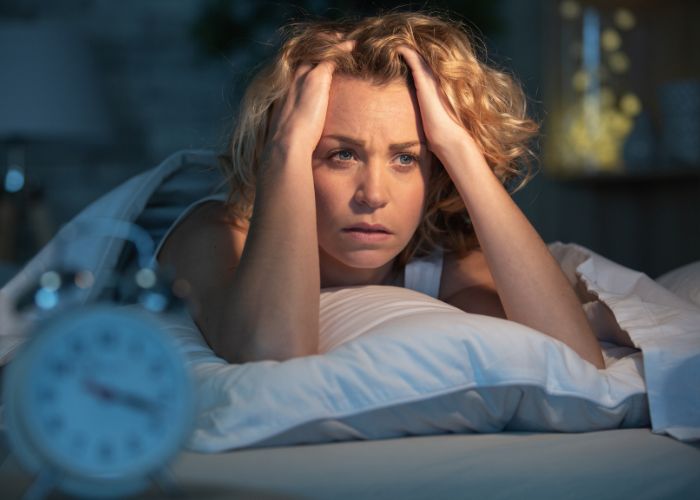
Nocturnal hypertension, or high blood pressure at night, often goes unnoticed. However, persistently elevated blood pressure can have a detrimental effect on your overall health. Learn more about three complications of nocturnal hypertension.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Events
Nocturnal hypertension is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke. While different times of day affect blood pressure, your BP should gradually lower at night in a process called nocturnal dipping.
In general, your blood pressure should be lower while you sleep and as your body rests. However, in people with nocturnal hypertension, the heart continues working hard during sleep, straining the cardiovascular system over time.
Impaired Sleep Quality
Impaired sleep quality is another complication of nocturnal hypertension. Symptoms of high blood pressure at night may include frequent awakening and poor breathing.
Furthermore, people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) have an increased chance of experiencing nocturnal hypertension. OSA is characterized by paused breathing during sleep. Combining OSA and high nocturnal blood pressure can impair sleep quality more drastically.
Kidney Failure and Disease
The kidneys’ most known function is to filter waste and excess fluid from the body. However, the kidneys also release many hormones, including renin, which helps regulate blood pressure.
A dense network of blood vessels supplies the kidneys with high volumes of blood. High blood pressure can damage the vessels around the kidneys and cause a decrease in blood volume. Low blood volume harms the kidneys and makes them less effective at filtering blood and regulating blood pressure, further worsening the effects of nocturnal hypertension.
High blood pressure at night can cause an increased risk of cardiovascular events, impaired sleep quality, and damaged kidney function. Addressing nocturnal blood pressure begins with a diagnosis.
Your doctor can give you an ambulatory blood pressure monitor that measures and records your blood pressure as you sleep. The data collected can help your doctor provide an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment course. Based on your doctor’s recommendations, lifestyle changes and the right medication can greatly improve health outcomes.